Cable Lug Types and Size Chart
What is the cable lug?
Cable lugs are vital components utilized in electrical systems to establish connections between cables and devices or equipment. They are available in a variety of materials, such as copper, tinned copper, brass, aluminum, and bi-metallic variants, and come in diverse sizes and shapes. The primary purpose of cable lugs is to ensure secure and reliable connections that facilitate optimal electrical flow while mitigating potential hazards like short circuits or fires. These versatile components find applications across various industries including power distribution, renewable energy systems, the automotive sector, as well as the marine industry. Acquiring a fundamental understanding of cable lugs is imperative for selecting the appropriate type based on specific application requirements while ensuring the utmost performance and safety.

What types of Cable Lugs does it have?
According to the material classification, there are Copper, Tinned Copper, Brass, Aluminum, and Bi-Metallic.
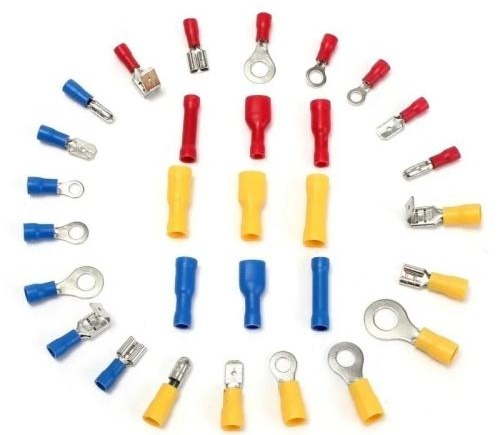
Cable lugs are available in a variety of materials, each possessing its distinct properties and advantages. The most prevalent types of cable lugs include copper, tinned copper, brass, aluminum, and bi-metallic options.
Copper cable lugs exhibit exceptional conductivity and corrosion resistance, rendering them ideal for high-performance applications.
Tinned copper lugs are coated with a layer of tin to provide added protection against corrosion while enhancing their conductivity.
Brass cable lugs offer durability and high-temperature resistance, making them suitable for harsh environments.
Aluminum cable lugs are lightweight and cost-effective, making them a popular choice for larger installations.
Bi-metallic cable lugs combine the benefits of two materials such as copper and aluminum to establish a robust and reliable connection.
This section will delve into the various types of available cable lugs along with their unique features and advantages.

According to the connection classification, there are soldering types, single crimping types, and successive crimping types.
The soldering type involves melting a metal alloy to join lug and wire together, which is commonly used in electronic devices.

Single crimping type refers to the terminal that is a individually isolated terminal, it has to be crimped one by one.

The successive crimping type involves a lug terminal without an isolated jacket to cover the feet, typically in roll form, which can be crimped by an automatic machine.

Each type has its advantages and disadvantages depending on the specific requirements of the application at hand. It is important to carefully consider which method will provide the most effective and efficient solution for each situation.
How to Measure Cable Lug Size?
The process of measuring the cable lug size is straightforward. It involves determining both the cable diameter and the dimensions of the attachment hole in the terminal. To ensure utmost accuracy, it is recommended to utilize a caliper or gauge for precise measurements.
Applications of Cable Lugs
- Power Distribution
- Renewable Energy Systems
- Automotive and Marine Industries
Cable lugs are essential for optimal electrical performance and safety in power distribution, renewable energy systems, automotive, and marine industries. They connect cables to transformers, solar panels, batteries, engines, and other components. In power distribution, cable lugs ensure stable and reliable energy transfer. In renewable energy systems, they enable the storage and conversion of renewable energy. Additionally, cable lugs provide secure connections for electrical systems in the automotive and marine industries.
Cable Lugs Size Chart




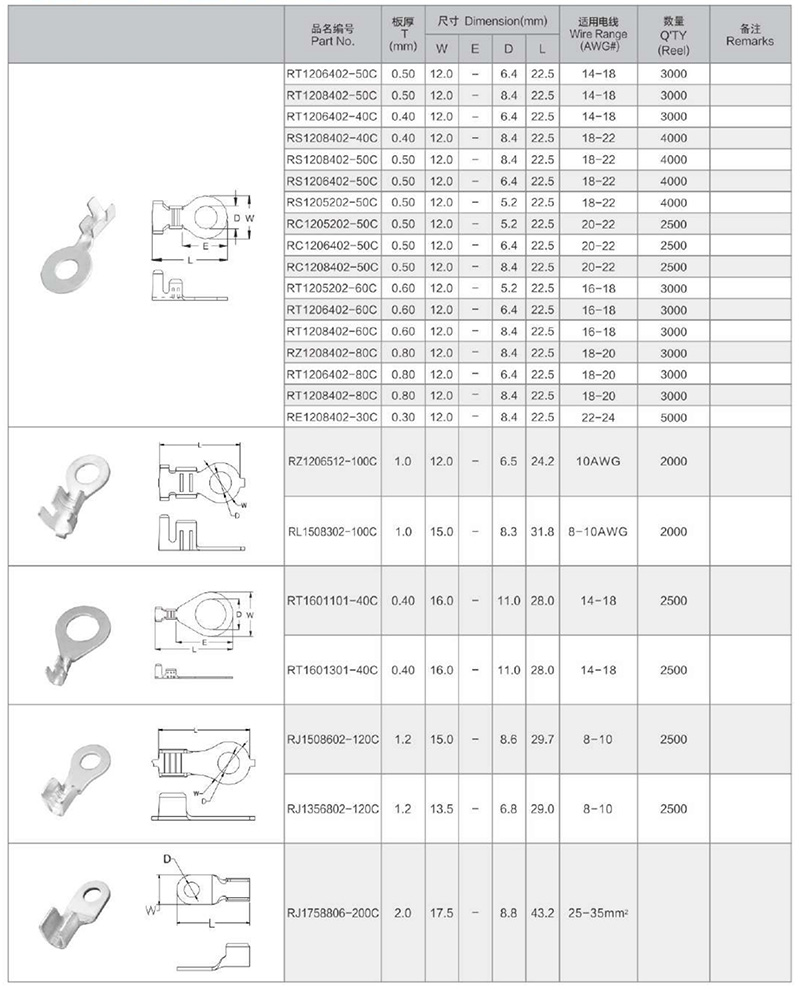



If you want to know more, please contact us to for ask a free catalog.
Summary
Although cable lugs are widely used for electrical connections, more robust versions are used to anchor non-electrical cables to surfaces, mounting plates, or other cables. Architectural stabilization and safety cables, as well as rigging, are often fitted with load-bearing cable lugs made of steel or iron to secure cables and components. Cable connectors for electrical use that are not subject to tension are made of aluminum, brass, copper, or lead and are sometimes plated to optimize voltage transfer and inhibit metal oxidation.
Cable lugs can be found on the wiring systems of automobiles, electrical boxes, machinery, household appliances, electronics, and other durable goods. For electrical use, cable lugs are typically insulated with rubber or plastic to prevent accidental transference of electricity to people or nearby electrical components. Other types require no insulation due to either cable lug placement or the lack of voltage.
