Automotive high voltage harness and electric vehicle charging harness
As we all know, in the field of new energy vehicle charging piles, wire harnesses can generally be divided into two categories:
1. The wiring harness represented by the electric vehicle interior, the packaged high voltage harness, and the low voltage harness can be classified into one type;
2. The charging harness can be divided into another category.
What is an automotive high-voltage wire harness?
An automotive high-voltage harness is a specialized wiring assembly used in electric and hybrid vehicles to safely transmit high-voltage electricity between different components of the vehicle's powertrain. These harnesses are critical for the efficient and safe operation of electric powertrains and usually consist of multiple cables, connectors, and protective coverings designed to handle high voltages, often ranging from several hundred volts to over a thousand volts.

The high-voltage wire harness can be divided into motor HV wiring harness, battery high voltage cable, and fast charging high voltage cables, etc. It mainly provides high-voltage power supply for new energy vehicles. The design of the wiring harness is therefore critical to ensure that it can withstand the high voltages and currents that are encountered in the vehicle. Its design mainly involves the working voltage, working temperature, temperature rise, wire diameter, cable protection, and the selection of high-voltage connectors.
|
Cable Cross-sectional Area (mm²) |
Safe Current Carrying Capacity (A) |
| 6 | 50 |
| 10 | 70 |
| 16 | 100 |
| 25 | 125 |
| 35 | 150 |
| 50 | 200 |
| 70 | 250 |
| 95 | 280 |
| 120 | 320 |
what is a charging cable?
A charging cable, often referred to as a charging wire harness, is an assembly of wires and connectors used in electric and hybrid vehicles to facilitate the safe and efficient transfer of electrical power from an external charging source to the vehicle's battery pack. This harness is a crucial component of the vehicle's charging system, ensuring that electrical energy is delivered correctly and safely.
Charging cable can be divided into two types.
- AC Charging cables
- DC Charging cables

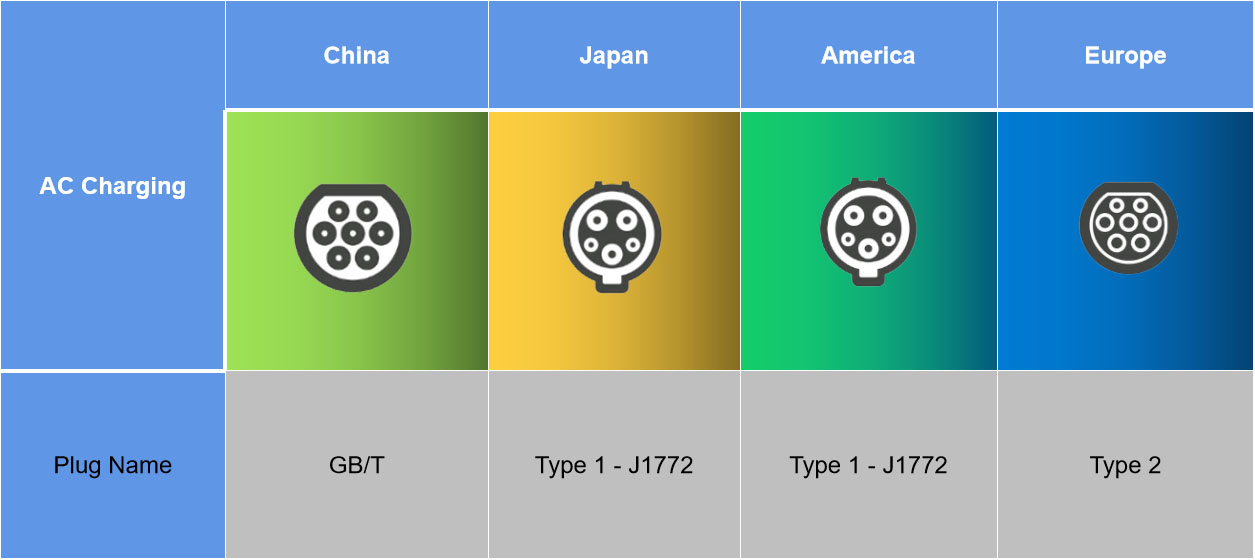
AC Charging Cables Connector Types
SAE Type 1 J1772 Connector
The J1772 is by far the most common electric vehicle AC charging connector type in the US, Canada and Japan. The connector has five pins: two main pins for power, one main pin for ground, and the other two smaller pins for safety and communication. It is compatible with Level 1 or Level 2 charging stations, charging at up to 80 amps. You can find J1772 charging stations at most gas stations and shopping centers where there are electric vehicle charging stations installed.
GB/T Connector
GB/T was developed by China's State Grid Corporation to help facilitate the use of electric vehicles across China's vast network of electricity networks.
Type 2 Connector
Type 2 connectors are usually found on the European market, and they have a larger connector head. This type of connector is also referred to as Mennekes, but it is not compatible with Type 1 connectors. It incorporates a locking mechanism to ensure that the charger and vehicle are properly connected.
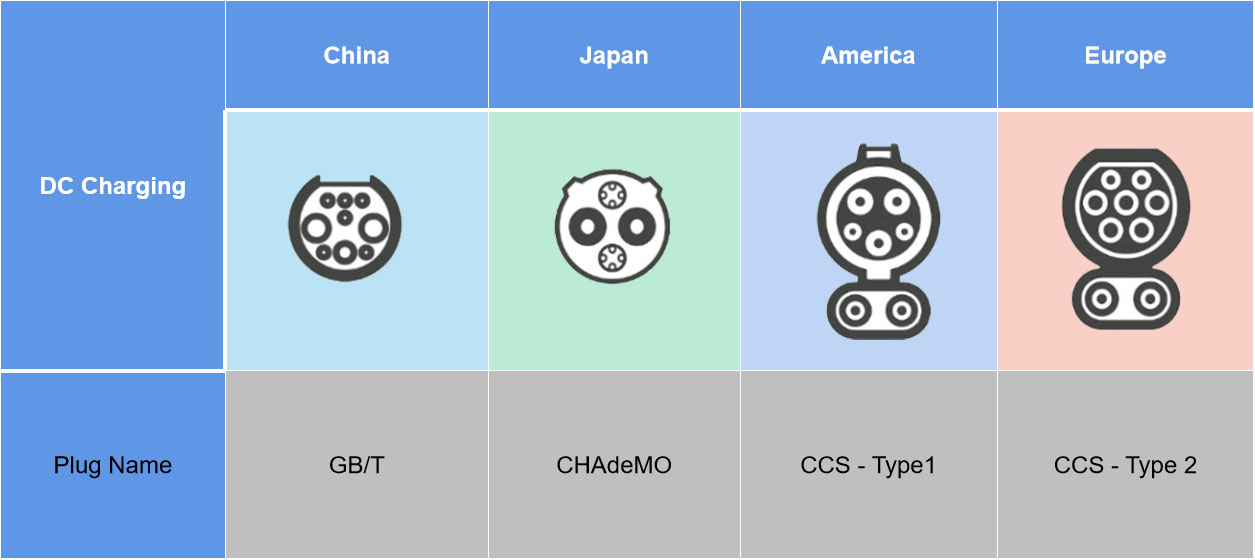
DC Charging Cables Connector Types
GB/T Connector
The GB/T connector is a Chinese standard for DC charging. It is currently used by BYD and other automakers in China. It can charge at up to 250 kW.
CHAdeMO
CHAdeMO (Charge de Move) is an abbreviation for "CHArge de MOve", which comes from the English words Charge and Move. The CHAdeMO DC Charging connector is used in Japan for high-power DC Fast Charging. It supports up to 50 kW of power delivery and can charge a car from 0% - 80% in 30 minutes or less!
CCS1 Connector
The most common DC charging connector is the CCS1 (Combined Charging Standard 1). The CCS1 connector is used in North America and it can deliver up to 350 kW and up to 350 amps of current. It is an extension of the J1772 standard AC charging connector, which is used for level 2 charging.
CCS2 Connector
The Combo 2-in-1 Charging Connector is a combination of AC/DC charging ports on one side. They are available in 60A to 200A. This type of connector is usually deployed at home or public charging stations that support DC Fast Charging (DCFC).
Tesla Supercharger
The Tesla Supercharger is a proprietary direct current fast charging (DCFC) network for Tesla vehicles. It is a proprietary system designed, built, and installed by Tesla Inc., using a 480-volt three-phase AC source that can deliver up to around 170 kW of power to the car, depending on location.
So, what is the difference between a high-voltage harness and an electric vehicle charging harness?
1, Laying different
Harness laying is usually the way a harness arrives from a distribution box and reaches an electrical device or another distribution box. The wire harness changes depending on the nature of the different environmental conditions.
The high-voltage harness of the car belongs to the fixed laying, but the static bending radius of each point is small; the charging harness belongs to the mobile laying, and the dynamic bending radius is small.
2, The heat resistance is different
The higher the heat resistance of the high-voltage wire harness of the car, the better the heat resistance and the higher the load-bearing capacity, so the starting point is 125 degrees, the height is 180 degrees (silicone rubber), 200 degrees (fluoro rubber); the charging harness is generally exposed outside. Do not get too hot, do not exceed 70 degrees, otherwise it will cause burns.
3, Different requirements for EMI
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is a comprehensive assessment of electromagnetic field interference (EMI) and immunity to interference (EMS) of electronic products. It is one of the most important indicators of product quality. Electromagnetic compatibility measurements include test sites and test instruments.
In order not to affect the communication control function of the vehicle, the high-voltage harness of the vehicle has high requirements on EMI and must meet the EMC standard of the vehicle; when the vehicle is charging, the vehicle stops, the charging harness does not need to meet the EMC standard of the vehicle, and only needs to meet the relevant environment. EMC. Standards such as gas stations, and residential community standards.
4, Different protection measures
The necessary protective measures should be taken around the high-voltage harness of the car to ensure the safety of both passengers and the vehicle itself. These measures include insulation materials, grounding systems, and proper shielding to prevent any electrical leakage or short circuits. Additionally, regular maintenance and inspections are crucial to identify any potential issues or damages in the harness. On the other hand, although the charging harness does not require specific protective measures like high-voltage harnesses do, it still needs to withstand various shocks and ultraviolet radiation. This is because, during charging processes, there might be accidental impacts or exposure to sunlight that could potentially damage the charging harness if it is not durable enough. To address these challenges, manufacturers often use robust materials such as reinforced plastics or rubber for charging harnesses. They also incorporate UV-resistant coatings or sheaths to protect against harmful ultraviolet radiation from sunlight. Furthermore, rigorous testing procedures are conducted on these components to ensure their reliability under different environmental conditions.
5, Physical performance requirements are different
The high-voltage harness of the car needs to meet the wear requirements of the car; the charging harness must meet the anti-rolling requirements of the moving harness. In order to ensure optimal performance and safety, both types of harnesses must be designed and manufactured with precision.
When it comes to the high-voltage harness, its primary function is to transmit electricity from the power source to various components in an efficient manner. As such, it needs to withstand constant use and potential wear caused by vibrations, temperature changes, and other environmental factors. The materials used in its construction should be durable and resistant to abrasion, ensuring a long lifespan without compromising electrical conductivity.
On the other hand, the charging harness plays a critical role in providing a stable connection between external power sources and electric vehicles during charging. To prevent any rolling or movement that could potentially damage or disconnect this vital link, anti-rolling measures are implemented within its design. This ensures that even when subjected to motion or external forces while on the go, such as driving over uneven terrain or sudden braking maneuvers, there will be no disruption in the power supply.
6, Different chemical resistance
The high-voltage harness of the car is designed to withstand a variety of liquids that may come into contact with it while driving. This includes everything from spilled drinks and rainwater to engine fluids and battery acid. The harness is made from durable materials that can resist corrosion, abrasion, and other forms of damage.
Similarly, the charging harness for electric cars must be able to withstand exposure to various liquids in the living environment outside the car. This could include rainwater, snowmelt, or even accidental spills from cleaning products or other household chemicals. To ensure safety and reliability, these harnesses are also constructed using high-quality materials that can resist wear and tear over time.
7, Different size requirements
The high-voltage harness of the car is limited by space and has a strict size. The smaller the size, the better. This constraint on size is crucial as it allows for efficient utilization of space within the vehicle, ensuring that all components are properly integrated without compromising safety or performance.
On the other hand, when it comes to the charging harness, there are no such limitations on size. Unlike the high-voltage harness which needs to fit into specific areas within the car's structure, the charging harness can be made thicker and larger if necessary. This flexibility in design allows for enhanced durability and robustness in handling higher currents during charging processes.
By having a larger charging harness, manufacturers can ensure improved power transmission efficiency while minimizing energy losses due to resistance. Additionally, a larger cross-sectional area of conductors in the charging harness reduces heat generation during operation, contributing to overall system reliability.
Furthermore, with advancements in technology and increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs), there is ongoing research and development focused on optimizing both high-voltage and charging harnesses. Engineers strive to find innovative solutions that strike a balance between compactness and performance while adhering to safety standards.
8, Different color requirements
Internationally, the color of the car's high-voltage harness being orange is a standard practice that has been adopted by many countries. This helps to ensure consistency and safety in the manufacturing process as well as during maintenance and repairs. It also makes it easier for technicians to identify and work with high-voltage components, reducing the risk of accidents or damage to equipment. And there is no need to change the color of the charge harness.
9, The number of cores is different
For ease of laying, the high-voltage harness of the car is usually a single core; the charging harness is usually a multi-core integrated wiring harness with high-voltage main and ground lines, low-voltage signal lines, and even communication double-effect lines (CAN). ).
10, Different international standards
International standards for automotive production lines are established by ISO organizations; international standards for charging lines are developed by IEC organizations.
Why are Electric Vehicle High Voltage Cables Orange?
The orange color of electric vehicle high voltage cables indicates their extremely high voltage, which can reach up to 1200V. They are also known as high-tension cables. The color orange warns people about high voltages, helping them avoid contact and reduce the risk of injury or death. High-voltage cables carry large amounts of power and can be dangerous if touched by people or animals. Orange, combined with other safety features on these cables, ensures that accidental contact is prevented.
When you look at a high-voltage cable, you see a bundle of wires inside a protective sheath that conducts electricity from one point to another. Each wire consists of smaller strands wound in a helix pattern and covered with insulating material to prevent electrical current from escaping into the surrounding air or materials. If there's any chance you might come into contact with high-voltage cables, make sure to wear rubber gloves, thick leather gloves, or thick rubber sleeves on your hands when working near them. And remember, never touch or go near exposed parts of the cable. The color of high-voltage cables has been standardized for many years now, and all manufacturers are required to adhere to this standard to ensure clear identification of orange cables in various workplaces or other settings.
The National Electrical Code (NEC) has designated orange as the color for high-voltage cables, according to the publication of the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). The NEC guides safe practices in various aspects of electrical usage. High-voltage cables are utilized for transmitting electricity at voltages exceeding 750 volts. Compliance with NEC regulations necessitates marking these cables by either wrapping them with orange tape or insulating them using an orange insulation sleeve. This requirement aims to alert individuals who may come into contact with these cables, enabling them to avoid potential injuries caused by physical contact.
Hooha Harness Introduction
Hooha Harness is a professional manufacturer in China, offering comprehensive OEM and ODM services. With over 20 years of experience in customizing wire harnesses, we have gained extensive expertise and knowledge in this field. Our team strictly adheres to the IPC/WHMA-A-620 standard, ensuring that our products meet the highest quality requirements. To further demonstrate our commitment to excellence, we have obtained prestigious certifications such as IATF16949, ISO9001, and UL certificates. These certifications validate our dedication to producing top-notch wire harnesses that comply with international standards.
At Hooha Harness, we specialize in designing and manufacturing custom automotive wire harnesses, molded cables, and power cables. Whether you need a specific wiring solution for your vehicle or require customized cable assemblies for industrial applications, we have the capabilities to fulfill your requirements. We take pride in providing exceptional customer service throughout every step of the process. From initial consultation to final delivery, our team works closely with clients to understand their unique needs and deliver tailored solutions promptly.
If you are interested in partnering with us or would like a free quote for your wire harness project, please do not hesitate to contact us now. Simply send us your wire harness drawing or specifications so that our experienced engineers can provide you with an accurate quotation based on your exact requirements.
We provide the following HV connection solutions
- New energy passenger car HV connection wire harness
- HV electrical connection wire harness for high-end commercial buses
- Truck HV electrical connection wire harness
- Motorhome HV electrical connection wire harness
- HV electrical connection wire harness for construction machinery and vehicles
- HV electrical connection wire harness for sanitation vehicles
- HV connection wire harness of energy storage system

FPIC 1500V HV Energy Storage Connector Harness

High volt wire harness

HV Wire Harness

electric vehicle power harness

New Energy Car Wiring Harness

New Energy Electric Vehicle Three-Phase Power Cable
How to customize your wire harness?
Send your sample or drawing/schematic for quote price→ Feedback with quotation(1~3 days) → Confirm quotation → Arrange sample you for approval→ [Make mold if needed (7 days) →Mold test] → Making samples(1~3 days)→Samples test(Approval) →place order for Mass production(2~3 weeks)→Quality checking→Packing →Delivery →After Service →Repeat Order.
